content.md 3.3 KB
%%LOGO%%
What Is CrateDB?
CrateDB is a distributed SQL database that makes it simple to store and analyze massive amounts of machine data in real-time.
CrateDB offers the scalability and flexibility typically associated with a NoSQL database, is designed to run on inexpensive commodity servers and can be deployed and run on any sort of network - from personal computers to multi-region hybrid clouds.
The smallest CrateDB clusters can easily ingest tens of thousands of records per second. The data can be queried, ad-hoc, in parallel across the whole cluster in real time.
Features
- Standard SQL plus dynamic schemas, queryable objects, geospatial features, time series data, first-class BLOB support, and realtime full-text search.
- Dynamic schemas, queryable objects, geospatial features, time series data support, and realtime full-text search providing functionality for handling both relational and document oriented nested data structures.
- Horizontally scalable, highly available and fault tolerant clusters that run very well in virtualized and containerised environments.
- Extremely fast distributed query execution.
- Auto-partitioning, auto-sharding, and auto-replication.
- Self-healing and auto-rebalancing.
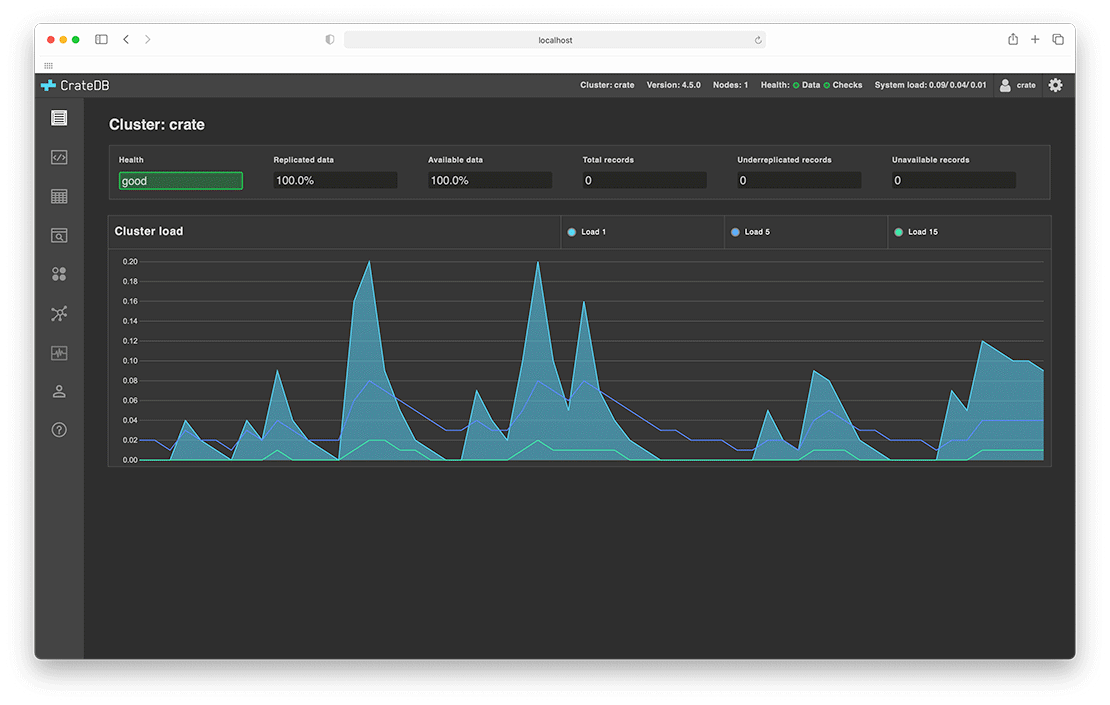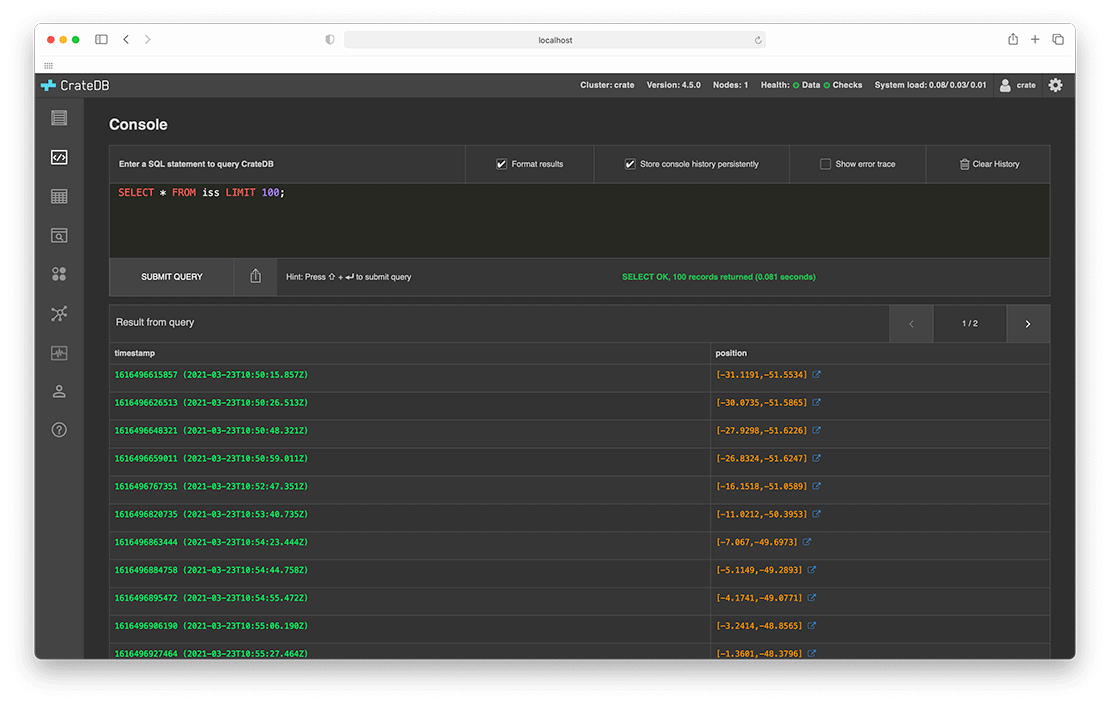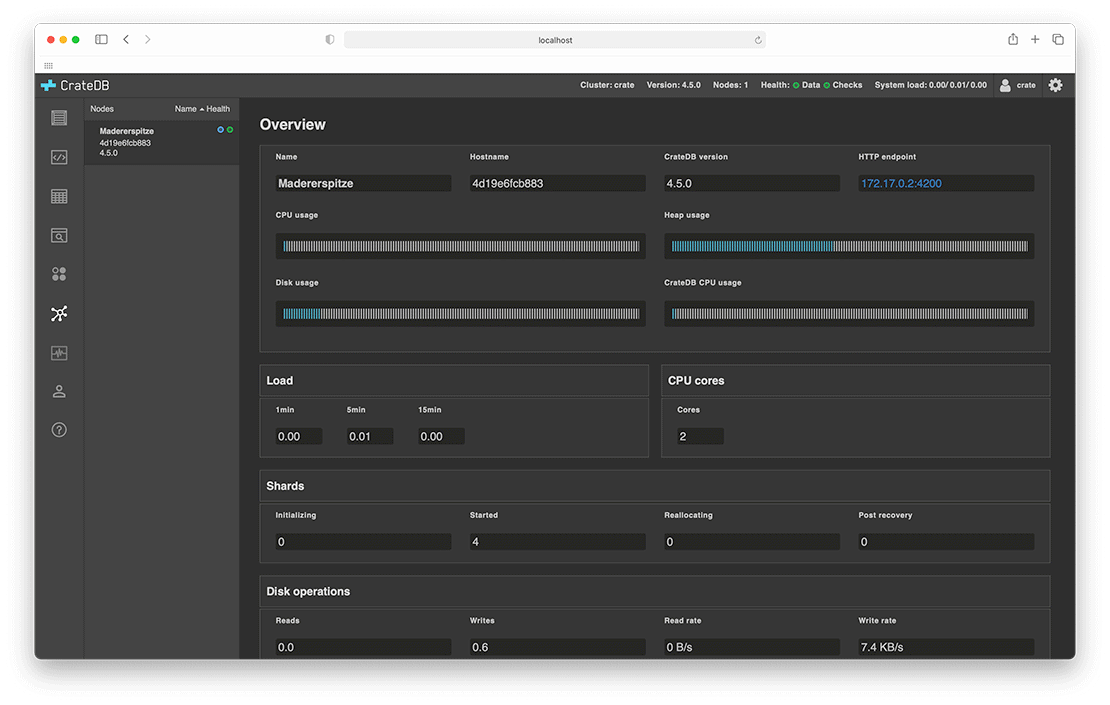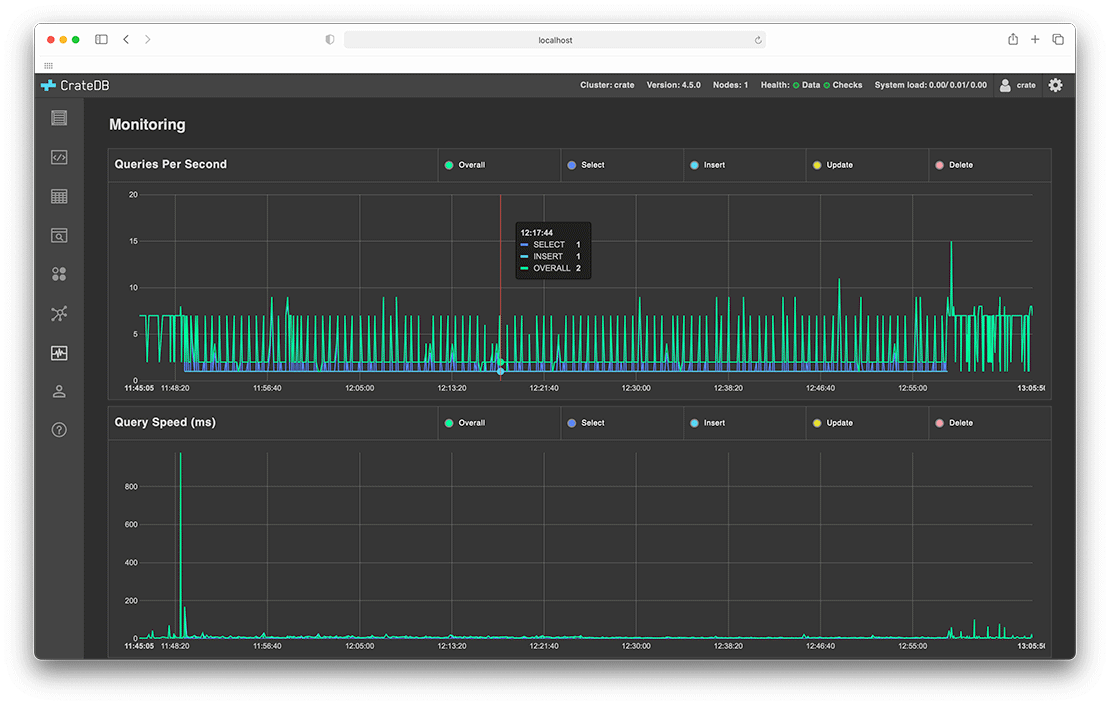
Screenshots
CrateDB provides an Admin UI:
Try CrateDB
Spin up this Docker image like so:
$ docker run --publish 4200:4200 --publish 5432:5432 %%IMAGE%% -Cdiscovery.type=single-node
Visit the getting started page to see all the available download and install options.
Once you're up and running, head over to the introductory docs. To interact with CrateDB, you can use the Admin UI web console or the CrateDB shell CLI tool. Alternatively, review the list of recommended clients and tools that work with CrateDB.
For container-specific documentation, check out the CrateDB on Docker how-to guide or the CrateDB on Kubernetes how-to guide.
Issues
Memory Accounting
The combinations of Linux kernel version 3.x and Docker >= 1.12 could lead to a major problem with memory accounting causing the kernel to kill the CrateDB process in the container. This problems occurs because of a slab shrinker issue that is fixed in kernel versions >= 4.0.
Others
For issue specific to the CrateDB Docker image, report issues via the docker-crate GitHub issue tracker
For issues with CrateDB itself, report issues via the crate GitHub issue tracker
Contributing
This image is primarily maintained by Crate.io, but we welcome community contributions!
See the contribution docs for more information.